Introduction
Electronic prescriptions offer a convenient alternative to paper prescriptions for patients. This page provides guidance to software developers who wish to build products that support electronic prescribing.
Pre-requisites
Conformance to the Healthcare Identifier Service (HI) is a prerequisite for prescribing and dispensing systems to participate in electronic prescribing.
Electronic Prescribing Conformance Process
The Australian Digital Health Agency (the Agency) offers a range of support services including consultations and information sessions. For support with the Agency's conformance requirements or technical specifications, please email help@digitalhealth.gov.au(link sends email).
Follow the steps below to get started.
Step 1: Achieve Healthcare Identifiers (HI) Service conformance
If your product is not yet conformant with the HI Service, please develop this capability first. For instructions please go to the following page:
If your product is already HI Service conformant please proceed to step 2.
Step 2: Understand Electronic Prescribing
To understand electronic prescribing, please read the Electronic Prescribing Technical Framework documents detailing the Solution Architecture, Conformance Assessment Scheme and Conformance Profile located here:
The Conformance Test Specification is located here:
Once you have read these documents, proceed to step 3.
Step 3: Your Product’s Role in Electronic Prescribing
Identify the functions your product will carry out in the electronic prescribing process and whether it needs to connect to the National Prescription Delivery Service (NPDS) to enable end-to-end electronic prescription transactions.
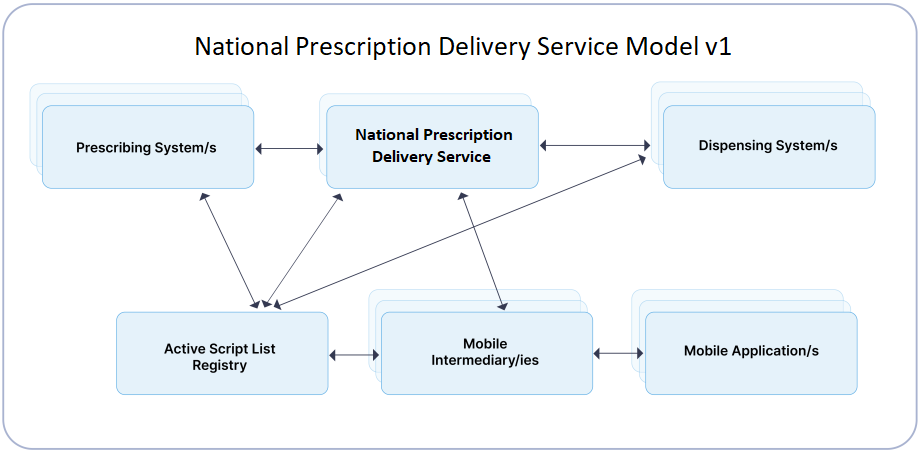
Most prescribing and dispensing Clinical Information Systems (CIS) will connect to the NPDS.
Hospital CIS solutions may provide their own direct PDS solution.
To use the Active Script List (ASL) your system will need to connect to the NPDS. The ASL is not available in a direct PDS model.
Step 4: Finalise the conformance process
Complete the conformance process with the NPDS and the Agency. The process varies depending on the type of product you are developing. It typically takes 20 business days to complete the process with the Agency. This time is in addition to product development, testing, self-assessment, and the observed testing session with the NPDS. An overview of the process steps, who performs each step, and the average time taken to complete is outlined below.
Conformance process timeline
Developer guides
Electronic Prescribing - CIS to NPDS or ASLR
The following steps will assist prescribing and dispensing Clinical Information System (CIS) software developers connect to the National Prescription Delivery Service (NPDS) and declare software conformance with the Agency’s Electronic Prescribing technical framework.
Electronic Prescribing - NPDS and ASLR
The following steps will assist software developers who provide National Prescription Delivery Service (NPDS) and/or Active Script List Registry capabilities to declare software conformance with the Agency’s Electronic Prescribing technical framework.
Electronic Prescribing - CIS with a Direct PDS
The following steps will assist Clinical Information System (CIS) software developers with a direct Prescription Delivery Service (PDS), declare software conformance with Australia Digital Health Agency (the Agency’s) Electronic Prescribing technical framework.
Electronic Prescribing - Mobile Intermediary System - Conformance Process
A mobile intermediary system is a software product that a mobile application uses to connect to, and interact with, the National Prescription Delivery Service (NPDS) and/or Active Script List Registry (ASLR).
Electronic Prescribing - Mobile Applications - Conformance Process
A mobile application or web-based application can be used by a subject of care or carer to manage prescriptions and to present an electronic prescription token to a pharmacy.
Electronic Prescribing – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Electronic Prescribing Frequently Asked Questions covering topics such as Prescribing Systems, Dispensing Systems, Mobile Applications, Mobile Intermediaries, Transitional eNRMC and Conformance Profile and more.
HI Service - Additional requirements for Electronic Prescribing
This guide discusses potential changes required in your software.
Software Developer Impact Roadmap
This roadmap has been developed to capture known impacts to software developers across participating government organisations.
NASH SHA-2 Certificates - Developer Guide
This developer guide is for developers whose products connect to the HI Service, My Health Record, electronic prescribing and secure messaging using a NASH (National Authentication Service for Health) PKI certificate.
Electronic Prescribing Sunset Dates for Conformance Profiles
The Australian Digital Health Agency (the Agency) has published a series of Electronic Prescribing (EP) Conformance Profiles (CP) with incremental increases in functionality.
Pharmacist Shared Medicines List (PSML)
The Pharmacist Shared Medicines List (PSML) is a clinical document type supported by the My Health Record system.